LATERAL SCAPULA
Radiological protocol for true lateral scapula projection
Demonstrated Pathology
Main indications: Fractures and dislocations of the proximal humerus and scapula.
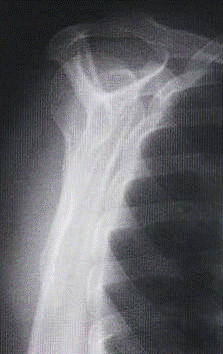
Anterior Dislocations
The humeral head will be seen below the coracoid process.
Characteristic position of an anteriorized humeral head.
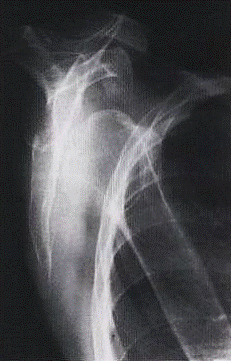
Posterior Dislocations
In posterior dislocations (less frequent), the humeral head will be seen below the acromion.
Characteristic position of a posteriorized humeral head.
Exposure Factors
Low exposure: Optimal parameters for lateral scapula visualization
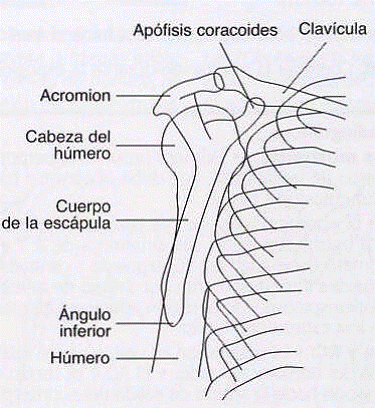
Visible Anatomical Structure
The following must be clearly observed:
- True lateral of the scapula
- Full proximal humerus
- Scapulohumeral joint
- Scapular profile without superimposition
- Humeral head-glenoid relationship
Cassette Size and Orientation
Longitudinal orientation to cover the full scapula and proximal humerus
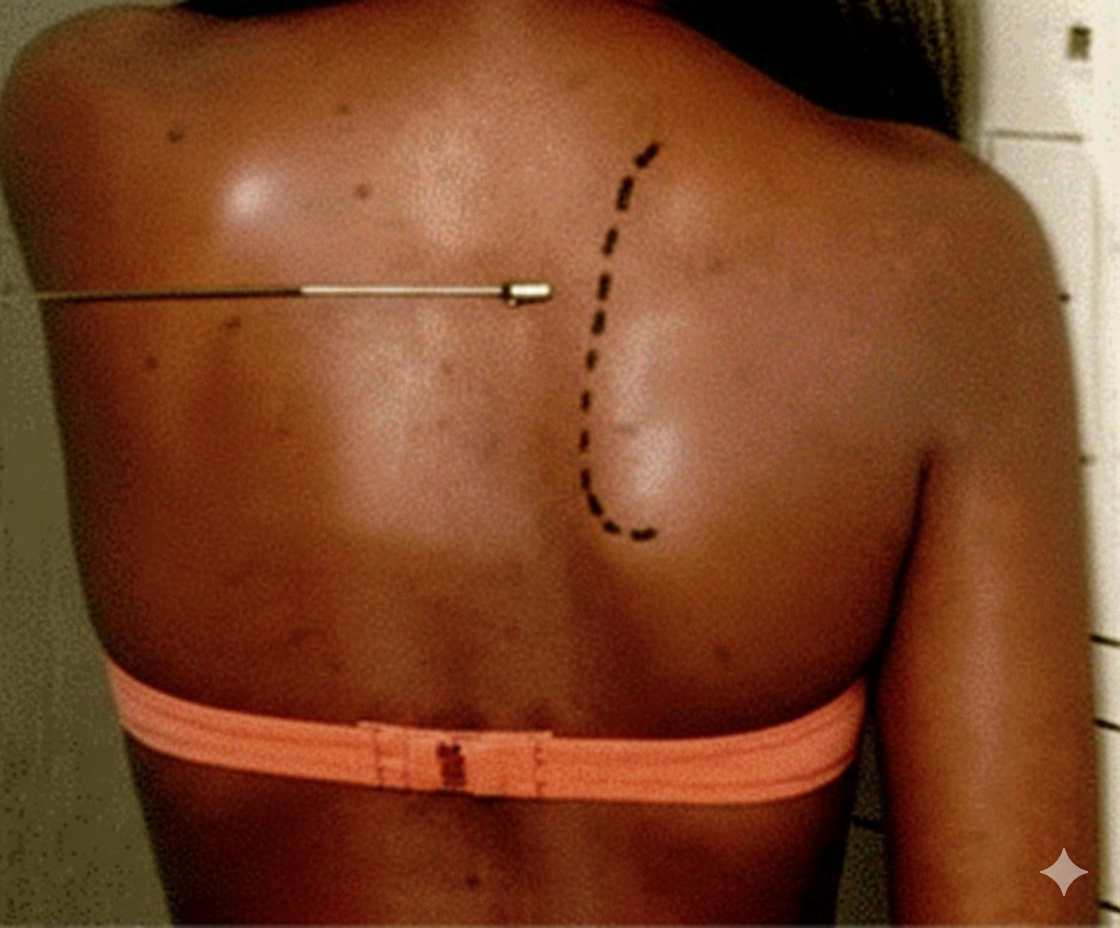
Patient Positioning
Central Ray Point
Direction: Perpendicular to the bucky
Location: Directed to the scapulohumeral joint, 5-6 cm below the shoulder
Importance of Correct Positioning
This projection is crucial for:
- Evaluating the humeral head-glenoid relationship in dislocations
- Visualizing fractures of the surgical neck of the humerus
- Identifying fractures of the scapular body
- Differentiating anterior vs posterior dislocations
Key: The 45-60° anterior oblique position is essential to obtain a true lateral scapula
Patient Instructions
"Hold your breath during the exposure"
Maintain position without movement and apnea during the radiographic exposure
Special Technical Considerations
Slight arm abduction
Prevents humerus-rib superimposition
Scapular palpation
Determines correct rotation
Do not rotate arm
Maintains natural position
45-60° Angle
Optimal anterior oblique position
Common Technical Challenges
Frequent problems in lateral scapula projection:
- Insufficient oblique position failing to achieve a true lateral
- Humerus-rib superimposition due to insufficient abduction
- Excessive arm rotation altering the joint relationship
- Difficulty palpating scapular borders in obese patients
Technical Variations
Acute Pain Patient
Minimize movement of the affected arm, position with maximum possible comfort.
Geriatric Patient
Consider mobility limitations; may require a smaller oblique angle.
Pediatric Patient
Reduce exposure according to age and ALARA protocol, adjust angle according to size.